A typical monitor consumes between 15 to 60 watts of power, depending on the size, technology, and usage settings. On average, most modern screens use around 20 to 30 watts during regular operation, making them relatively energy-efficient compared to older models. To put it simply, your monitor’s power consumption isn’t just about saving energy; it’s also about influencing your electricity bills and environmental footprint.
In just a few hours of daily use, a monitor can significantly contribute to your household’s energy consumption. Understanding how much power your monitor uses helps you make smarter choices, whether you’re aiming to reduce costs or lessen your ecological impact. From tiny portable screens to large gaming displays, power usage varies, but staying informed allows you to optimize your setup for both performance and efficiency.
How Much Power Does a Monitor Use?
Understanding how much power a monitor consumes is important for saving energy and reducing electricity bills. Monitors come in various sizes and types, each with different energy demands. Knowing the average power usage helps you choose the right monitor for your needs and budget.
Factors Affecting Monitor Power Consumption
Several factors influence how much power a monitor uses. These include size, type, brightness settings, and usage patterns. Smaller screens typically consume less power than larger ones, making them more energy-efficient.
Monitor Size and Resolution
Size is a key factor in power consumption. A 21-inch monitor uses less energy compared to a 32-inch or larger screen. Higher resolution monitors like 4K or QHD often require more power to display detailed images and videos.
For example, a 24-inch Full HD monitor might use around 20 watts during active use, while a 27-inch 4K monitor could consume 30 watts or more.
Display Technology
Different display technologies impact energy use significantly. LCD monitors with LED backlighting are generally more energy-efficient than older CCFL backlit LCDs. OLED monitors can produce deep blacks but may have higher power consumption in certain scenarios.
LED-backlit LCDs are popular for their balance of performance and power efficiency, making them suitable for everyday use.
Power Usage in Different Monitor Types
Monitors come in various types, each with distinct power consumption profiles. Here is a breakdown of common types:
| Monitor Type | Average Power Consumption | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| LCD with LED Backlighting | 20-40 watts | Most energy-efficient and widely used |
| OLED Monitors | 30-60 watts | Produces deep blacks but can consume more energy in bright scenes |
| Older LCD with CCFL Backlight | 50-80 watts | Less energy-efficient, phased out in favor of LED models |
| Gaming Monitors | 30-80 watts | Higher refresh rates and brightness increase power use |
Impact of Brightness and Settings on Power Consumption
Adjusting your monitor’s brightness affects how much power it consumes. Higher brightness levels increase energy use, while dimmer settings save power.
Many monitors include power-saving modes that automatically reduce brightness or turn off certain features when inactive. Using these features can lower overall consumption.
Brightness Levels
Typically, increasing brightness by 50% can raise power consumption by around 20%. Lowering brightness saves energy and extends the lifespan of the display.
For example, a monitor running at maximum brightness may use 30 watts, but at minimum brightness, it might only use 20 watts.
Power Saving Features
Features like sleep mode or automatic shut-off help decrease power consumption when the monitor is not in use. Enabling these features ensures your monitor isn’t wasting electricity.
Most modern monitors automatically enter a low-power state after a period of inactivity, saving energy and reducing costs.
Energy Consumption in Standby and Idle Modes
Monitors continue to use some power even when turned off but in standby or sleep mode. This “phantom” energy consumption can add up over time.
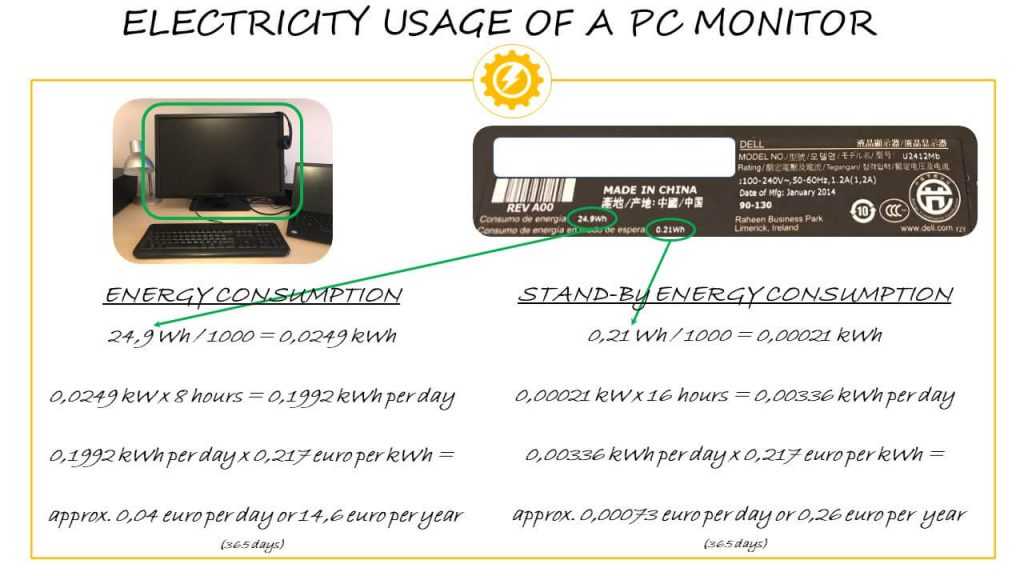
Standby mode typically uses between 0.5 to 3 watts, depending on the monitor model. To save energy, it’s best to completely turn off monitors when not in use for extended periods.
Measuring the Power Usage of Your Monitor
To get an exact idea of how much power your monitor uses, you can use a power meter. Plugging your monitor into a device like a Kill-A-Watt meter provides real-time energy consumption data.
This helps you compare different monitors and optimize your setup for energy efficiency, ultimately saving money and reducing environmental impact.
Comparing Power Usage of Different Monitor Sizes and Types
Here’s a simple comparison to give you an overview of what to expect in terms of power consumption:
- Small Monitors (19-22 inches): 15-25 watts
- Standard Monitors (24-27 inches): 20-40 watts
- Large Monitors (32 inches and above): 40-70+ watts
- Gaming and High-Performance Monitors: 30-80+ watts depending on features
How to Reduce Power Consumption of Your Monitor
Lowering your monitor’s energy use can be simple and effective. Start by adjusting brightness, using power-saving modes, and turning off your monitor when not in use.
Additionally, consider replacing older monitors with newer, energy-efficient models. Using a smart power strip can also help turn off multiple devices at once, saving energy and reducing clutter.
Additional Tips for Energy Efficiency
- Optimize your display settings for balance between visibility and power use
- Enable automatic sleep or hibernate modes when your work is done
- Regularly clean your monitor to keep it running smoothly and efficiently
- Invest in monitors with Energy Star certification for best efficiency
Related Topics
Understanding how much power a monitor uses is just part of managing your overall tech energy footprint. You can also explore topics like energy-efficient computers, cost-effective peripherals, and sustainable technology habits.
Monitoring your overall energy consumption helps identify other areas to save, such as printers, speakers, or routers.
Knowing the typical power usage of a monitor guides you in making smart choices. Whether you’re selecting a new monitor or trying to reduce your electricity bills, this knowledge empowers you to operate more efficiently and environmentally conscious. By adjusting settings and choosing the right device, you can enjoy your display while minimizing energy waste.
How to Monitor Electricity Use | This Old House
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the amount of power a monitor consumes?
The power consumption of a monitor varies based on its size, display technology, brightness settings, and usage patterns. Larger screens and models with higher resolutions tend to use more power. Additionally, display technologies like OLED or LED can affect energy use. Adjusting brightness levels or enabling power-saving modes can significantly reduce energy consumption during use.
How does screen resolution impact the power usage of a monitor?
Higher screen resolutions require more processing power, which in turn increases the monitor’s energy consumption. For example, 4K monitors generally use more energy than Full HD displays because they process and display more detailed images. However, the difference may be minimal with energy-efficient models and proper power management settings.
Can enabling power-saving features reduce a monitor’s energy consumption?
Yes, enabling power-saving or eco modes on your monitor can significantly lower electricity usage. These features reduce brightness and disable unnecessary functions when idle or during low activity periods, helping to conserve energy without compromising overall display quality.
Are modern monitors generally more energy-efficient than older models?
Yes, newer monitors often incorporate advanced technologies designed to decrease power consumption. LED backlighting and energy-efficient display panels help reduce electricity use compared to older CCFL or CRT monitors. Manufacturers also include features that optimize power use, making modern models more environmentally friendly.
What is the typical power range for most computer monitors?
The majority of standard monitors consume between 20 to 60 watts during typical operation. Smaller or energy-efficient models may use around 15 watts, while larger, high-resolution monitors can draw over 70 watts under full brightness. Using power management settings can help keep consumption within an efficient range.
Final Thoughts
A monitor’s power consumption varies depending on size, type, and usage. On average, an LED monitor uses about 20-30 watts, while larger or older models may draw 50 watts or more.
Energy-efficient monitors help reduce electricity bills and environmental impact. Always check the specifications for exact power usage details.
How much power does a monitor use? It depends on factors like screen brightness and resolution, but most modern devices are designed to be energy-conscious. Being aware of these details helps you make smarter choices for your setup.
I’m passionate about hardware, especially laptops, monitors, and home office gear. I share reviews and practical advice to help readers choose the right devices and get the best performance.