Quick fix: Restart your router, check for interference, update firmware, and reset settings. These simple steps often resolve 2.4GHz Wi-Fi issues quickly and effectively.
When your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi connection suddenly drops or stops working, it can be incredibly frustrating—especially when you rely on it for daily browsing, streaming, or work from home. Many users face this problem without understanding why it happens or how to fix it. The good news is that most 2.4GHz Wi-Fi issues are easily resolved by troubleshooting common causes such as interference from other devices, outdated firmware, or misconfigured settings. By following some straightforward steps, you can restore your connection without needing technical expertise. This article will guide you through practical solutions to get your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi back up and running smoothly, so you can stay connected without hassle.
Router 2.4GHz WiFi Not Working Fix: A Complete Guide to Troubleshooting and Resolving the Issue
Understanding the 2.4GHz WiFi Band
The 2.4GHz band is one of the two primary frequency bands used by routers to broadcast WiFi signals. It offers a larger coverage area compared to the 5GHz band, making it ideal for devices farther from the router. However, it can be prone to interference from other devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth gadgets. Recognizing how this band works sets the foundation for troubleshooting WiFi problems effectively.
Common Reasons Why 2.4GHz WiFi Stops Working
Several issues can cause your 2.4GHz WiFi to stop functioning properly. These include:
- Interference from other electronic devices
- Outdated or incorrect router firmware
- Incorrect WiFi settings or channel selection
- Hardware failure or physical damage to the router
- Overcrowding on the network with too many connected devices
- Distance and obstructions between the router and devices
Identifying the root cause helps in selecting the correct troubleshooting steps.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting to Fix 2.4GHz WiFi Issues
The following steps guide you through resolving common problems with 2.4GHz WiFi connectivity.
1. Restart Your Router and Devices
A simple restart can resolve temporary glitches. Turn off the router and the device experiencing connectivity issues. Wait for about 30 seconds, then turn both on again. This refreshes network connections and clears minor bugs.
2. Check the WiFi Settings on Your Router
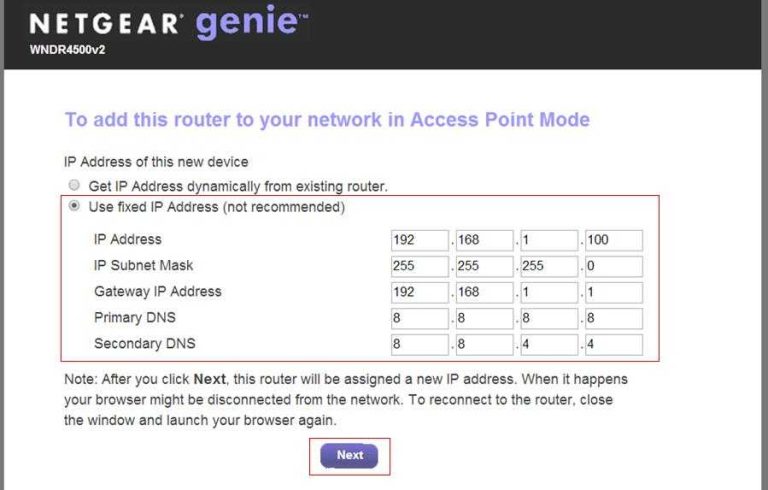
Log into your router’s admin panel using your browser. Usually, you can do this by entering the router’s IP address, often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Verify that the 2.4GHz band is enabled and broadcasting. Ensure the SSID (network name) is visible and the network password is correct.
3. Change the WiFi Channel
Interference from neighboring networks can cause disruptions. Access the WiFi settings and try switching the channel. Popular channels include 1, 6, and 11. Use a WiFi analyzer app to identify less crowded channels for better performance.
4. Update Firmware of Your Router
Manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that improve stability and fix bugs. Visit the router manufacturer’s website, download the latest firmware, and follow instructions for installation. Keeping firmware current is crucial for optimal performance.
5. Check for Interference from Other Devices
Electronics like microwave ovens and cordless phones operate on 2.4GHz and can interfere with the WiFi signal. Keep your router away from such devices and ensure other electronics are functioning properly.
6. Adjust the Placement of Your Router
Physical obstructions like walls, furniture, or appliances can weaken the WiFi signal. Place your router in an open, elevated spot central to your devices. Avoid placing it inside cabinets or near metallic objects.
7. Reset Network Settings on Your Devices
Sometimes, device-specific issues cause connectivity problems. On your smartphone or computer, reset network settings or forget and re-connect to the WiFi network. This clears potential configuration errors.
8. Check for Overloaded Network
Too many connected devices can slow down or disrupt WiFi. Disconnect unused devices and limit the number of gadgets using the 2.4GHz network simultaneously. Consider upgrading your plan if multiple users need high bandwidth.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If basic steps do not resolve the issue, consider more in-depth solutions.
1. Disable and Re-enable the 2.4GHz Band
In your router’s admin panel, temporarily disable the 2.4GHz band, wait a few seconds, and then re-enable. This can reset the band and fix stubborn issues.
2. Factory Reset Your Router
A factory reset erases all custom settings and restores default configurations. Use a paperclip to press and hold the reset button for about 10-15 seconds. Reconfigure your network afterward.
3. Check for Hardware Problems
Inspect the router for physical issues such as damaged antennas or overheating. If the router is old or physically damaged, replacing it may be the best solution.
Related Topics for Better WiFi Performance
Optimizing your WiFi involves more than fixing issues. Consider these additional tips:
- Using WiFi extenders or mesh systems to improve coverage
- Switching to a dual-band router for better device management
- Enabling Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize important traffic
- Regularly updating device drivers and firmware
- Implementing strong security measures to prevent unauthorized access
Technical Tools to Help Troubleshoot WiFi Problems
Use these tools to diagnose network issues:
- WiFi analyzer apps for channel and interference detection
- Ping tests to identify latency problems
- Speed test websites to check actual internet speeds
- Router logs to review error messages and alerts
These tools provide insights into your network health, making troubleshooting more efficient.
Final Tips to Maintain a Healthy 2.4GHz WiFi Connection
Regular maintenance can prevent future problems. Schedule periodic restarts of your router. Keep your firmware updated, and monitor interference sources nearby. Proper placement and device management ensure stable connections over time.
The intricate balance of managing interference, configurations, and hardware health plays a crucial role in maintaining a reliable 2.4GHz WiFi network. Carefully following these steps will significantly improve your network stability and device connectivity.
Turn OFF 5 GHz WiFi to Connect Smart Devices
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I reset my router to resolve connectivity issues on the 2.4GHz band?
If your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi isn’t working, try resetting your router by unplugging it from the power source, waiting for about 10 seconds, then plugging it back in. Allow the router to fully restart and check if the signal is restored. This simple step refreshes the network settings and can often fix temporary glitches.
What are some troubleshooting steps if my 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is slow or unstable?
Start by moving closer to your router to see if signal strength improves. Check for interference from other electronic devices like cordless phones or microwave ovens. Updating your router’s firmware can also improve performance. Additionally, ensure your devices are connected to the correct frequency band and restart the router to refresh the connection.
How do I change the Wi-Fi channel on my router to avoid interference?
Access your router’s admin panel through a web browser using its IP address. Log in with your credentials, then navigate to the wireless settings section. Locate the channel selection options for the 2.4GHz band and choose a less congested channel, such as 1, 6, or 11. Save the settings and restart your router if needed to apply the changes.
What should I do if my device cannot detect the 2.4GHz network?
Ensure that the 2.4GHz band is enabled in your router’s settings. Check if the network SSID is broadcasted; if not, enable SSID broadcast to make it visible. Also, verify that your device is compatible with the 2.4GHz band and is within range. Restarting both your device and the router can help establish the connection.
Are there specific firmware updates that can fix 2.4GHz Wi-Fi issues?
Yes, firmware updates often include fixes for known Wi-Fi problems, including those affecting the 2.4GHz band. Visit your router manufacturer’s website to find the latest firmware version compatible with your device. Follow the instructions provided for updating the firmware safely, and ensure your router remains powered during the process.
Final Thoughts
The issue with your router 2.4ghz wifi not working fix often involves simple troubleshooting steps. Restart your router to resolve temporary glitches, and check if the 2.4GHz band is enabled in settings. Updating firmware can also improve performance and stability. Ensuring your device is within range prevents signal interference and connection issues. Following these tips helps restore reliable Wi-Fi, making your network function seamlessly again.

I specialize in process engineering and system optimization. I enjoy writing guides that simplify troubleshooting and help improve efficiency in everyday tech use.