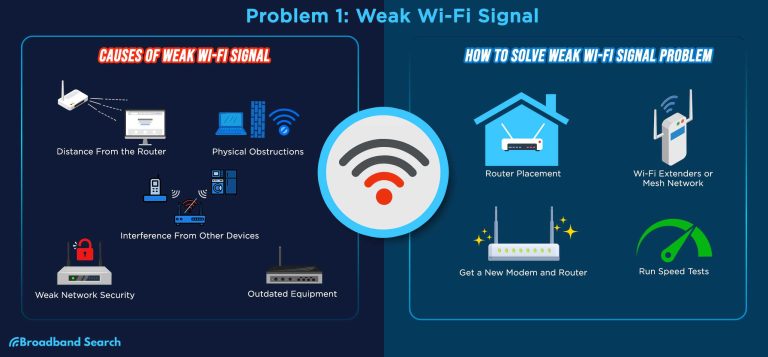
A quick fix for a router antenna not working is to restart your router, check the antenna connection, and ensure it’s properly aligned. Sometimes, simply repositioning the antenna or resetting your device can restore optimal connectivity.
If your router antenna suddenly stops working, don’t panic. There are simple steps you can take to troubleshoot and fix the issue without calling a technician. Starting with a reboot often clears minor glitches. Ensuring the antenna is firmly connected and positioned correctly can make a big difference. Sometimes, antennas can become loose or damaged over time, affecting signal strength. In more stubborn cases, updating your router’s firmware or replacing the antenna might be necessary. This article explores easy-to-follow solutions to get your router transmitting signals effectively again, so you can enjoy a stable internet connection. Whether you’re at home or in the office, fixing your router antenna can be quicker than you think.
Router Antenna Not Working Solution: How to Fix Your Wi-Fi Signal
Understanding Why Your Router Antenna Stops Working
Many factors can cause your router antenna to stop functioning properly. Sometimes, physical damage happens due to drops or impacts, which can break the antenna. Other times, software glitches or outdated firmware can impair the antenna’s performance. Identifying the root cause is essential before attempting repairs or adjustments.
Check Physical Connections and Damage
Start by inspecting your router’s antenna carefully. Ensure that it is securely attached to the router’s port. Look for visible signs of damage like cracks, bends, or corrosion. If the antenna is loose or damaged, replacing it might be necessary to restore proper signal strength.
Steps for Physical Inspection
- Unplug the router from power to avoid electrical hazards.
- Remove the antenna gently if it’s detachable.
- Examine the antenna and connection port for visible damage or dirt.
- Clean the connection points with a soft cloth if needed.
- Reconnect the antenna firmly and test the Wi-Fi signal again.
Reposition and Optimize Your Router Antenna
The orientation and placement of your router antenna can significantly influence Wi-Fi coverage. A poorly positioned antenna may lead to weak signals or dead zones. Adjust the antenna to different angles to find the best coverage.
Best Practices for Antenna Placement
- Position the antenna vertically for optimal coverage in most cases.
- Place the router in a central location within your home or office.
- Avoid placing the router near metal objects, thick walls, or electronic devices that cause interference.
- Elevate the router on a bookshelf or high surface for better signal distribution.
Update Router Firmware and Settings
Firmware updates can fix bugs and improve overall router performance, including antenna functionality. Check your router manufacturer’s website regularly for updates. Updating firmware can often resolve issues caused by software glitches.
How to Update Firmware
- Log into your router’s admin panel through a web browser.
- Locate the firmware update section, usually under “Settings” or “Maintenance.”
- Download the latest firmware from the manufacturer’s website.
- Follow the instructions to upload and install the update.
- Reboot the router and test your Wi-Fi signal after updating.
Reset Your Router to Factory Settings
A factory reset can fix persistent software problems that affect antenna performance. Use a paperclip or similar object to press and hold the reset button on the back of the router for about 10 seconds. This process restores default settings and can resolve configuration conflicts.
Steps for a Proper Reset
- Ensure the router is plugged in and powered on.
- Press and hold the reset button with a toothpick or pin.
- Release the button when the router restarts, indicated by flashing lights.
- Reconfigure your network settings if needed.
- Test Wi-Fi coverage again after reset.
Replace the Router Antenna
If the antenna is physically damaged or no longer functions well, replacing it can be a straightforward solution. Many routers come with detachable antennas that are easy to swap out.
Choosing the Right Replacement Antenna
| Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Omnidirectional Antenna | Distributes Wi-Fi signals evenly in all directions | Great for covering large open areas |
| Directional Antenna | Focuses Wi-Fi signals in a specific direction | Improves signal strength over longer distances |
How to Replace Your Antenna
- Buy a compatible replacement antenna from an electronics retailer or online store.
- Turn off your router and unplug it from the power source.
- Unscrew the old antenna carefully from the connector.
- Attach the new antenna by screwing it into the connector securely.
- Power on the router and check for improved Wi-Fi signals.
Troubleshooting Interference and Signal Obstacles
Interference from other electronic devices or physical objects can make your router antenna seem non-functional. Identifying and minimizing interference enhances Wi-Fi strength.
Common Sources of Wi-Fi Interference
- Microwave ovens
- Wireless phones and baby monitors
- Bluetooth devices
- Other nearby Wi-Fi networks
- Metal furniture or appliances blocking signals
Solutions to Reduce Interference
- Place your router away from appliances and electronic devices that emit interference.
- Switch to a less congested Wi-Fi channel via router settings.
- Use 5 GHz Wi-Fi band if your device and router support it for less interference.
- Minimize physical barriers like thick walls or large metal objects between your router and devices.
Utilize External Antennas and Signal Boosters
External antennas can offer better coverage and stronger signals than built-in options. Signal boosters or Wi-Fi extenders help expand your network reach if the antenna cannot be repaired.
Adding External Antennas
Many routers support external antennas that can be upgraded for better performance. Choose antennas that match your router’s specifications for optimal results.
Using Wi-Fi Extenders and Signal Boosters
- Place extenders halfway between your router and areas with weak signals.
- Ensure compatibility with your existing router for proper functioning.
- Adjust the position of extenders for maximum coverage and speed.
Consider Upgrading Your Router
If your router is outdated or repair costs are high, replacing it with a new model may be the best solution. Modern routers often include advanced antennas and better signal distribution technology.
Features to Look for in a New Router
- Multiple high-gain external antennas
- Dual-band or tri-band Wi-Fi support
- Beamforming technology for focused signal transmission
- Gigabit Ethernet ports for fast wired connections
- Compatibility with the latest Wi-Fi standards (802.11ac, 802.11ax)
Steps to Set Up Your New Router
- Unbox the new router and connect it to your modem.
- Follow the setup instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- Configure Wi-Fi networks and security settings through the admin panel.
- Position the router in an optimal location and test Wi-Fi coverage.
Additional Tips for Maintaining Your Router Antenna
Regular maintenance can keep your router functioning well. Keep firmware updated, clean the device, and handle antennas gently.
Routine Care and Checks
- Keep the router in a dust-free environment.
- Check for firmware updates monthly.
- Rearrange the placement if Wi-Fi coverage drops over time.
- Protect your router from physical shocks to prevent antenna damage.
Addressing issues with your router antenna often doesn’t require professional repair. With careful inspection, proper placement, and timely upgrades, you can maintain strong Wi-Fi signals across your space. Remember that sometimes, replacing the antenna is the simplest and most effective fix for persistent problems. Consistent maintenance and avoiding interference are key to ensuring your network remains reliable and fast.
How to Fix and Upgrade a Weak WiFi Signal | Ask This Old House
Frequently Asked Questions
What steps can I take if my router’s antenna appears damaged or broken?
If your router’s antenna is visibly damaged or broken, first try to carefully inspect it for cracks, bends, or missing parts. If the damage is minor, gently realign or straighten the antenna. In cases of severe damage, it’s best to replace the antenna with a compatible one, which you can purchase from the manufacturer or authorized vendors. Avoid using the damaged antenna, as it may reduce signal strength or cause connectivity issues. Always handle antenna components with care to prevent further damage.
How can interference from other devices affect my router’s antenna performance?
Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, or wireless headsets, can interfere with your router’s antenna signals. These devices emit signals in similar frequency ranges, which can weaken or disrupt your Wi-Fi connection. To minimize interference, keep your router away from such devices, place it in an open area with minimal obstructions, and switch off nearby electronics when troubleshooting connection issues. Adjusting the position of your antenna can also help improve signal clarity and stability.
Is it necessary to replace my router to fix antenna issues?
Not always. If your router’s antenna isn’t functioning properly, try resetting or repositioning it first. Sometimes, simply adjusting the angle or height of the antenna can improve the signal. If these adjustments don’t help, check for firmware updates, as outdated software can cause performance problems. Only consider replacing the entire router if the antenna is damaged beyond repair, or if the device is outdated and no longer supports current technology standards. In many cases, replacing the antenna separately can restore optimal performance without buying a new router.
Can software settings impact the performance of my router’s antenna?
Yes, incorrect or misconfigured software settings can affect your router’s signal distribution. Ensure that your router’s wireless mode, channel, and bandwidth settings are properly configured. Using the default or auto settings can often optimize performance. Additionally, disabling any unnecessary features that might interfere with signal strength, like certain security options or guest networks, can improve overall connectivity. Regularly updating your router’s firmware also ensures that software-related issues are addressed, helping maintain strong signal performance.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the router antenna not working solution involves checking connections, adjusting antenna positions, and updating firmware. These steps often resolve common issues quickly. If problems persist, replacing the antenna or seeking professional help may be necessary. Proper troubleshooting ensures better signal strength and connectivity, enhancing your internet experience.

I specialize in process engineering and system optimization. I enjoy writing guides that simplify troubleshooting and help improve efficiency in everyday tech use.