When diving into the world of home networking, it’s easy to confuse WiFi and a router, but they serve distinct roles. In simple terms, WiFi is the technology that enables wireless devices to connect to a network, while a router is the hardware that facilitates the connection between your devices and the internet. Think of WiFi as the invisible pathway that allows your smartphone or laptop to communicate with your router, which in turn connects to your internet service provider. Understanding this difference is essential for troubleshooting connectivity issues or when upgrading your home network. With this clarity, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right equipment and enjoy a seamless online experience.
What is the Difference Between WiFi and Router
Understanding the difference between **WiFi** and a **router** is essential for anyone who uses the internet at home or in the office. While both terms are commonly heard, they refer to different components of your network system. This article will break down these concepts in a simple, clear manner.
What is WiFi?
WiFi is a technology that allows electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets, to connect to the internet wirelessly. It enables these devices to communicate with one another and access the web without needing physical cables.
WiFi works by using radio waves to transmit data. Think of it like a radio station sending signals. Your device picks up these signals and can then browse the internet, stream videos, and send emails.
How WiFi Works
WiFi networks are created using **access points**. These are devices that take your internet connection from a cable and distribute it wirelessly. The most common access point in homes is a router.
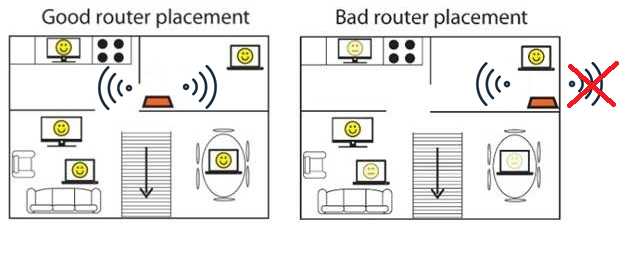
To connect to WiFi, devices must be within range of the access point. Most modern routers have a range of about 150 feet indoors and up to 300 feet outdoors, depending on the model.
What is a Router?
A router is a device that routes data from your internet connection to all the devices in your home or office. It acts as a traffic director, ensuring the correct information goes to the right device.
While many people think of a router as just a box with lights, it does much more. A router can connect multiple devices to the internet simultaneously, creating a local area network (LAN).
Types of Routers
There are several types of routers available:
- Wired Routers: These are connected directly to your internet modem with cables and distribute the connection to devices via Ethernet cables.
- Wireless Routers: These include built-in WiFi capabilities, allowing devices to connect wirelessly.
- Modem Routers: These combine a modem and router in one device, simplifying the setup process.
Key Differences Between WiFi and Router
Now that we’ve defined WiFi and routers, let’s dive into their key differences.
Functionality
– **WiFi**: WiFi is the method of connecting devices to the internet wirelessly.
– **Router**: A router is the device that manages the flow of data between your internet connection and your devices.
Physical vs. Wireless
– **WiFi**: WiFi represents a wireless connection, meaning no cables are necessary for data transmission.
– **Router**: A router can be wired or wireless, as it routes data through both methods.
Dependent Components
– **WiFi**: WiFi needs a router (or another access point) to function.
– **Router**: A router can provide internet access through wired connections, but its full capabilities are realized when paired with WiFi.
Importance of Both in Your Network
Both WiFi and routers play vital roles in your home or office network. Understanding how they work together is essential for optimizing your internet experience.
Enabling Connectivity
Roaming freely around your home with your smartphone or laptop is possible because of WiFi. Thanks to routers, you can have many devices connected at once without slowing down your internet speed.
Network Security
Routers have built-in security features to help protect your network. Features like firewalls and password settings can prevent unauthorized access. WiFi security protocols, such as WPA3, encrypt your data, making it difficult for potential intruders to intercept communication.
Common Misunderstandings
There are several misconceptions about WiFi and routers that can lead to confusion.
WiFi is Not the Same as Internet
While WiFi allows you to connect to the internet, it is not the internet itself. It is merely a medium to access the internet. Your router connects you to your internet service provider (ISP) to deliver data to your home.
All Routers Offer WiFi
Not all routers have WiFi capabilities. Some are designed solely for wired connections, such as those used in office environments where devices are hardwired for speed and stability.
Choosing the Right Router for Your Home
When selecting a router, consider several factors to ensure it meets your needs.
Speed
Look for a router that offers adequate speed for your internet plan. Most devices will list their speed capabilities in Mbps (megabits per second).
Range
Choose a router that provides a suitable range for your home size. Bigger homes may require additional access points or a mesh network to eliminate dead zones.
Security Features
Ensure your router comes with security options like WPA3 encryption for safety. Many modern routers offer additional security features like parental controls and guest networks.
Understanding the difference between WiFi and a router is crucial for effective internet use. WiFi enables wireless access to the internet, while a router directs that data to your devices. With the right knowledge, you can enhance your networking experience and ensure a stable, secure connection for all your devices. By investing in a quality router and understanding how WiFi works, you can optimize your internet performance and enjoy seamless connectivity.
Routers VS. Modems – What is the Difference Between a Router and a Modem? I Tech Talk
Frequently Asked Questions
“`html
What role does a router play in a Wi-Fi network?
A router connects multiple devices to a single internet connection and manages network traffic. It enables communication between devices within a local network and directs data packets to and from the internet. Without a router, devices would struggle to access the internet as they wouldn’t have a pathway to connect to the external network.
Can you connect a device directly to Wi-Fi without a router?
No, a router is essential for managing Wi-Fi connections. While some devices may connect directly to a modem for internet access, this setup limits the ability to connect multiple devices simultaneously. A router allows various devices to share the internet connection wirelessly while also providing additional features like security and network management.
How does Wi-Fi signal strength impact connectivity?
Wi-Fi signal strength significantly affects connectivity quality. A stronger signal results in faster data transfer rates and more reliable connections. On the other hand, weak signals can lead to slow internet speeds, dropped connections, and difficulties in streaming or gaming. Factors affecting signal strength include distance from the router, physical obstructions, and interference from other electronic devices.
Are Wi-Fi extenders different from routers?
Yes, Wi-Fi extenders serve a different purpose than routers. While routers establish and manage the Wi-Fi network, extenders amplify the existing Wi-Fi signal to expand coverage in larger spaces or areas with weak signals. They connect to the router wirelessly and help eliminate dead zones, providing better access to the network in hard-to-reach areas.
Is it possible to have multiple routers in a single network?
Yes, you can use multiple routers within a single network. This setup is useful for improving coverage in larger spaces or managing different network segments. When configuring multiple routers, ensure they are set up properly to avoid conflicts and maintain seamless connectivity throughout the network.
“`
Final Thoughts
WiFi refers to the technology that allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly. It works through radio waves, enabling seamless communication between devices and the internet.
A router, on the other hand, is the device that directs this internet traffic, connecting multiple devices to a single internet source.
In summary, the main difference between WiFi and a router is that WiFi is the wireless connection, while the router is the hardware that facilitates that connection. Understanding “what is the difference between wifi and router” helps clarify how these components work together to provide internet access.
I’m passionate about hardware, especially laptops, monitors, and home office gear. I share reviews and practical advice to help readers choose the right devices and get the best performance.